Why Most Treatments For Hand Pain Fail and Are Not Effective
Treatments For Hand Pain
Most treatment for hand pain fail because hand pain can be caused by inflammation or damage, such as from osteoarthritis (OA). This degenerative disorder results in the breakdown of cartilage in joints. Repetitive use or prolonged periods of inactivity can exacerbate joint symptoms. Even after undergoing conservative treatment, surgery should be considered if the symptoms persist. However, this option is rarely recommended due to the high risk of complications and severe side effects.
Steps of Treatments for Hand Pain
Most hand pain is not severe enough to require medical intervention. Treatment for stiffness and numbness can help ease the symptoms and improve function. But treatments for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis typically fail because the treatment is based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs rather than addressing the root cause of the problem. Surgical intervention is often required for severe diseases, including amputation.
Surgery is the last resort, but other treatments for hand pain may be necessary if the pain is severe. These include joint replacement, which involves inserting artificial implants to replace the damaged bone. While this treatment can improve function, it doesn’t fix the problem. Ultimately, surgery cannot solve the pain issue. Here are some effective treatment options for hand pain.
Surgical Procedure
Surgery can be used to treat hand pain. While it can be performed as a surgical procedure, it requires several steps, including stretching the finger. The most common surgery for hand pain is a corticosteroid injection. This treatment is generally non-invasive but may require a local anaesthetic and is a risky alternative. Side effects, such as infection, may also accompany the procedure.
Some cases of hand pain can be treated by taking anti-inflammatory medicines, or surgery may be necessary. In some cases, an injection with steroid medicine will help relieve the pain. In some cases, the doctor may recommend a surgical procedure. The surgeon will then perform the surgery. The most common options for hand pain are medications and surgical procedures. In addition to anti-inflammatory medicines, other methods are also available.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
In addition to surgical treatment, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also be used. Tylenol, for example, relieves pain but does not treat inflammation. In addition to splints and braces, prescription drugs may treat hand pain. In rare cases, surgery is needed to relieve the pain and restore function. While most treatments for hand pain fail, several other methods are worth exploring.
There are a variety of treatments for hand pain. In most cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will relieve pain. But these treatments are often ineffective for some people. In some cases, surgical procedures are necessary. If the pain is chronic or recurring, your doctor will recommend a treatment. Surgical treatment for hand pain may be the only option for you.
Most Common Treatment
Surgical treatment for hand pain is the most common treatment for the condition. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will reduce inflammation and pain, but they will not cure the problem. Some patients may require joint replacement surgery. Surgical treatments for hand pain should be considered only if the condition is a systemic disease that affects the hands. They must be diagnosed and treated immediately.
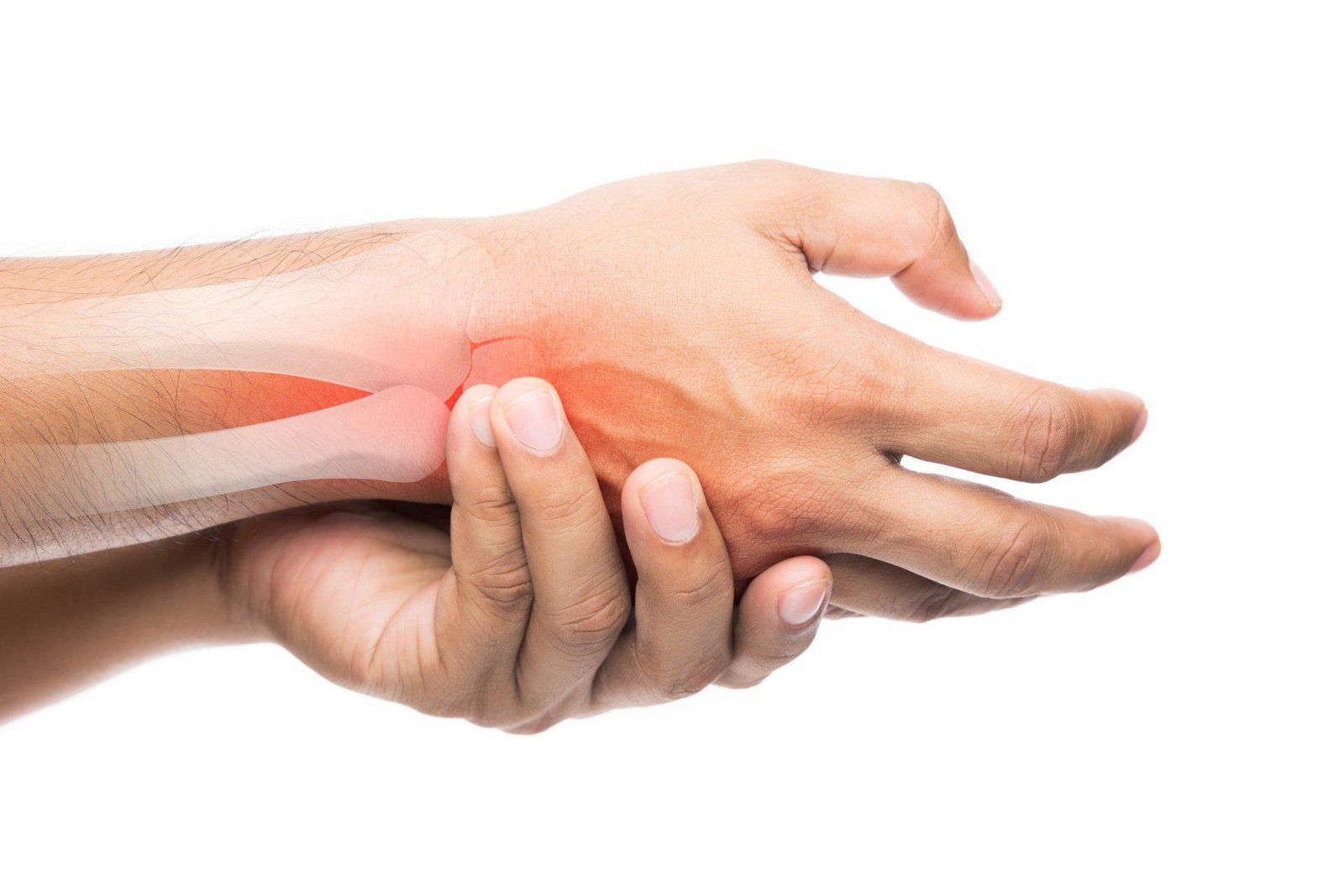
Injections of NSAIDs are another option. They are safe, effective, and don’t require surgery. NSAIDs can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation, but they are not the only treatment options for hand pain. In some cases, surgical treatments are needed to treat systemic diseases. If you’re seeking a non-surgical treatment for hand pain, you should consider a consultation with your doctor.
Final Thoughts
Surgical treatment is only a temporary solution. Most doctors will prescribe some form of NSAIDs, but they will not permanently remove the problem. In some cases, surgical procedures are needed. It is best to consult a doctor and undergo treatment in this case. Occupational therapy can teach you how to reduce the strain on your joints. Besides, occupational therapists can prescribe tools that will spare your joints.